Decoding Fertility Hormones: Your Roadmap To Conception
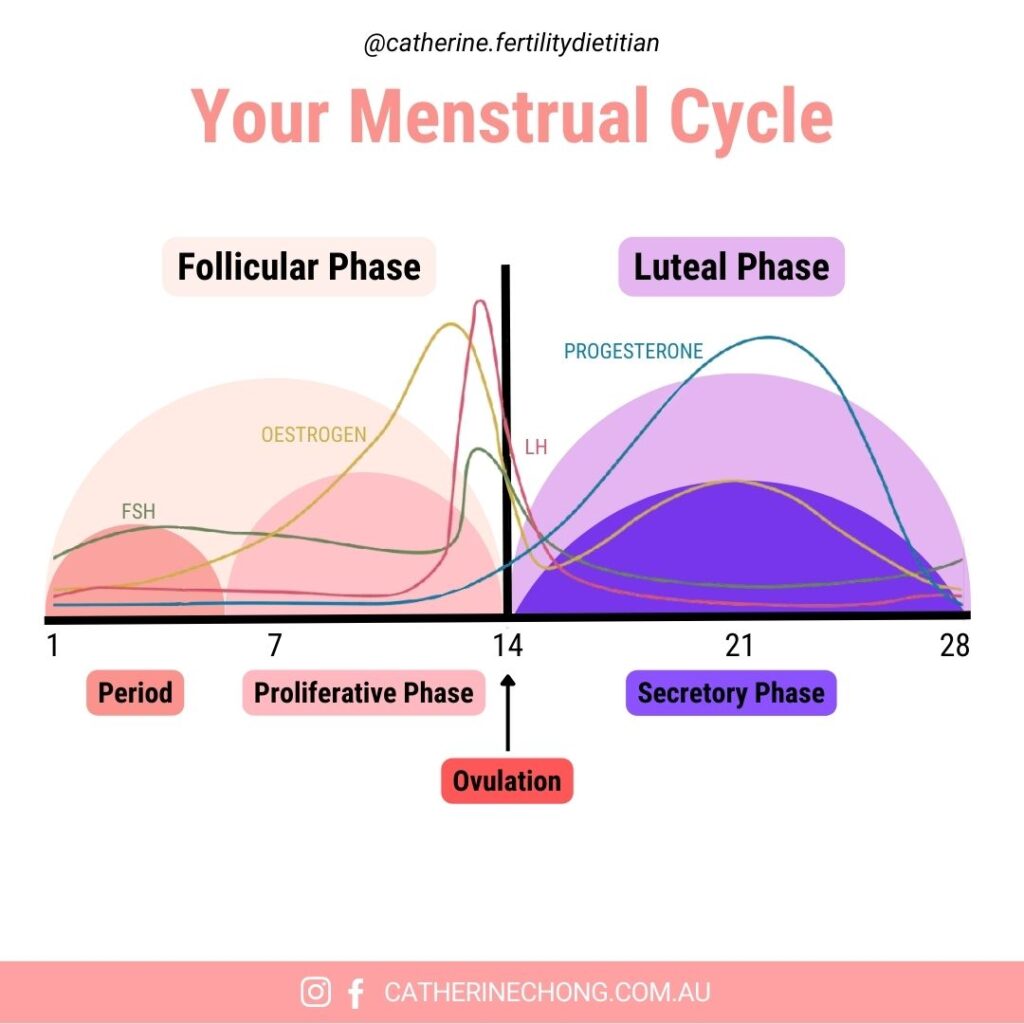
Fertility hormones serve as essential maestros, orchestrating the rhythmic fertility dance in women’s bodies, known as the menstrual cycle. This cyclical symphony of fertility, which unfolds monthly, is an intricate ensemble of hormonal shifts defined by two distinct movements: the follicular and luteal phases.
The harmonious interplay of four primary fertility hormones – oestrogen, luteinizing hormone, progesterone, and follicle-stimulating hormone – regulates the rhythm of this reproductive cycle. Comprehending these hormones’ distinct roles and collaborative interactions can be a game-changer for women trying to conceive.
The Fundamental Forces Behind Women’s Fertility
1. Follicle Stimulating Hormone
Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) is a critical fertility hormone, essential in the early stages of the reproductive cycle. Produced by the pituitary gland, FSH plays a pivotal role in overseeing the development of ovarian follicles, which are responsible for housing oocytes, the precursors to mature eggs.
The role of FSH is to stimulate the growth of many follicles within the ovaries. However, typically only one follicle dominates and matures fully.
During the early stages of the follicular phase and again in the follicular-luteal transition, FSH levels rise, creating an environment that nurtures the follicles. The increase in FSH levels also triggers the production of oestrogen.
2. Oestrogen
Oestrogen, primarily produced by the ovaries, is a powerful hormone that influences various aspects of the fertility cycle. At the beginning of the cycle, as the follicles mature, they produce increasing amounts of oestrogen.
The increase in oestradiol, a type of oestrogen, occurs post the emergence of the ovulatory dominant follicle and becomes more pronounced following the selection of the dominant follicle during the follicular phase.
Oestrogen also plays a crucial role in producing cervical mucus, facilitating sperm mobility and survival. As oestrogen levels rise, they reach a threshold that triggers a surge in luteinizing hormone.
3. Luteinizing hormone: The Trigger for Ovulation
Luteinizing Hormone (LH) is a hormone that surges during the middle of the menstrual cycle, typically around day 14 in a 28-day cycle.
The maturation of the ovarian follicles prompts the release of this hormone, setting the stage for the grand finale of the egg’s maturation and its subsequent release from the dominant follicle, a process referred to as ovulation.
Ovulation signifies the journey of an egg from the ovary into the fallopian tube, where it awaits potential fertilisation by sperm. The LH surge also acts as a catalyst, transforming the ruptured follicle into a temporary endocrine gland called the corpus luteum. This complex process underscores LH’s critical role in orchestrating the sequence of events in the fertility cycle.
4. Progesterone
Progesterone, produced by the corpus luteum after ovulation, plays a crucial role in the second half of the fertility cycle.
Progesterone helps prepare the uterus for the possible implantation of a fertilised egg by maintaining the thickened uterine lining, creating an environment conducive to embryo implantation.
Progesterone levels rise after ovulation and remain elevated throughout the cycle’s luteal phase. If fertilisation occurs, the corpus luteum produces progesterone to support early pregnancy.
If fertilisation does not occur, the corpus luteum disintegrates, and all hormone levels drop, causing the shedding of the uterine lining, resulting in menstruation.
Can You Influence Your Fertility Hormones?
Engaging in a balanced lifestyle plays a vital role in promoting the harmony of fertility hormones and enhancing overall reproductive health. Consistent exercise, a nutrition-rich diet, and effective stress management can contribute to an optimal equilibrium of these hormones.
Particularly, maintaining a balanced diet plays a significant role. Consuming various foods rich in antioxidants, fibre, and lean proteins can aid in regulating hormone levels, thereby contributing to a healthy fertility cycle.
Habits like cigarette smoking and alcohol consumption have been identified as disruptors to this hormonal balance and are best avoided for optimal reproductive health. Sufficient sleep is another pivotal aspect, supporting the body’s innate hormone regulation process.
The Bottom Line
- Understanding the intricate balance and roles of key fertility hormones can significantly influence the potential for conception.
- Maintaining a balanced lifestyle, including a nutritious diet, regular exercise, managing stress and adequate sleep, can positively influence fertility hormone balance and reproductive health.
Need More Help?
Are you seeking additional support and guidance in optimising your fertility through a personalised nutrition plan?
Schedule a nutrition consultation today and take the first step towards achieving your fertility goals.
You May Also Be Interested In
Disclaimer: Content on this website is provided for information purposes only and should not be replaced with medical advice. We recommend you discuss with your healthcare providers (doctor, dietitian, pharmacist, etc.) any medical questions for diagnosis and treatment, dietary plan, or use of any medications and nutritional supplements before you make any changes. DietitianChong Pty Ltd shall not bear any liability for reliance by any user on the materials contained on this website.







