Enhancing Fertility Naturally With Healthy Cervical Mucus Production
Healthy cervical mucus plays a crucial role in a woman’s fertility by providing a conducive environment for sperm survival and facilitating sperm transport to the egg.
Cervical mucus is a fluid that is produced and secreted by the cervix. Its characteristics, such as its colour, texture, moisture and amount secreted, vary in response to hormonal changes. These characteristics influence how easily sperm can move up the vagina and into the uterus.
How Does Cervical Mucus Change Throughout Our Menstrual Cycle?
Throughout the menstrual cycle, hormonal fluctuations influence the consistency and volume of cervical mucus, affecting fertility differently.
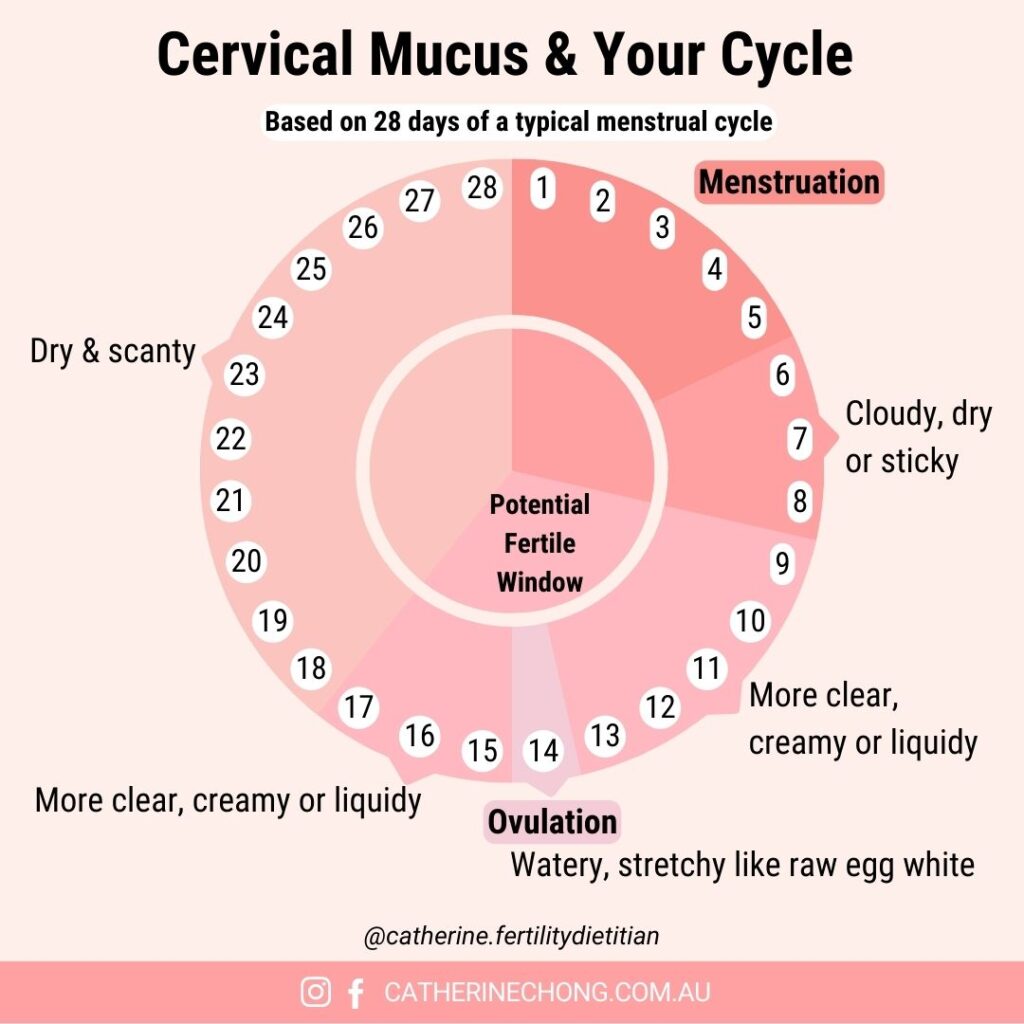
In the early stages of the cycle, cervical mucus is often minimal and thick, making it less hospitable for sperm. Before ovulation, estrogen levels rise, and this promotes healthy cervical mucus and increases secretion. The mucus becomes more abundant, clear, and slippery, resembling raw egg whites. This type of mucus, known as “fertile-quality cervical mucus,” creates a supportive environment for sperm by providing nourishment and protection and facilitating sperm movement toward the egg.
This optimal form of cervical mucus is believed to last approximately six days, known as the peak fertility period. During this time, the chances of conception are significantly higher due to the ideal consistency and volume of cervical mucus. After ovulation, progesterone levels rise, reducing cervical mucus secretions and returning to a thicker, less sperm-friendly consistency.
This shift in mucus quality indicates decreased fertility as the cycle progresses towards menstruation. Understanding these changes in cervical mucus and their relationship with hormonal fluctuations throughout the menstrual cycle can help women identify their fertile window and improve their chances of conception.
Here Are The Top 7 Ways To Boost Healthy Cervical Mucus:
1. Increase Hydration:
Staying well-hydrated is crucial for overall health and produces high-quality, healthy cervical mucus. This is because cervical mucus consists mainly of water, so when the body is dehydrated, it can directly impact the volume and texture of the mucus.
Throughout the period cycle, the level of hydration in cervical mucus varies. Insufficient hydration may lead to thicker, less abundant mucus, creating a challenging environment for sperm survival and movement. On the other hand, maintaining proper hydration helps to keep cervical mucus at the right consistency to support sperm and promote conception.
Aim for at least 8-10 glasses of water per day or more to ensure optimal hydration, depending on physical activity, climate, and individual needs. Keeping track of your water intake and making a conscious effort to drink water throughout the day can make a noticeable difference in the quality of your cervical mucus.
2. Healthy Carbohydrates
Interestingly, carbohydrates also affect how hydrated and effective your cervical mucus is during this fertile window. An older study found that increased carbohydrate consumption during ovulation helps the mucus retain more water. This hydration is crucial because it facilitates sperm migration, making it easier for sperm to reach the egg.

So it’s essential that you don’t try to exclude all the carbohydrate foods in your diet. Ensure that you include a healthy and balanced amount of healthy grains such as barley, quinoa, rolled oats, brown rice, whole-grain pasta, and whole-wheat flour bread.
3. Increase Vitamin C:
Vitamin C is essential for the production of healthy cervical mucus, and this is because of its antioxidative properties and its role in hormone production. As an antioxidant, vitamin C helps neutralise free radicals that can cause cellular damage, promoting overall reproductive health.
This, in turn, supports the optimal functioning of the reproductive system, including the production and maintenance of cervical mucus. Foods rich in vitamin C like oranges, grapefruits, and lemons; berries like strawberries and raspberries; tropical fruits like kiwi and papaya; and vegetables like bell peppers, broccoli, and kale.
4. Increase Vitamin E:
Vitamin E is vital for cervical mucus production and helps to keep the mucus thin and stretchy. This may be due to its role in regulating estrogen levels, a hormone that influences cervical mucus production. Higher estrogen levels are associated with increased cervical mucus secretion and improved quality, particularly in the fertile window preceding ovulation.

In addition, as an antioxidant, vitamin E helps to neutralise free radicals that can cause cellular damage. Some research found a relationship between low vitamin E levels and decreased cervical mucus secretions in women with unexplained infertility, further highlighting the potential importance of vitamin E in reproductive health. Good sources of vitamin E include sunflower seeds, almond nuts, olive oil, pine nuts and hard-boiled eggs.
5. Increase Zinc To Boost Healthy Cervical Mucus:
Zinc is essential for the production of healthy cervical mucus. One of the primary functions of zinc in fertility is its involvement in hormone regulation. Zinc is vital for synthesising, storing, and releasing essential reproductive hormones. By contributing to balanced hormone levels, zinc helps regulate the menstrual cycle, influencing the quality and consistency of cervical mucus throughout the cycle.
To ensure adequate zinc intake, incorporate various zinc-rich foods into your diet. Foods high in zinc include oysters, considered one of the best sources; red meat such as beef and lamb; poultry like chicken and turkey; nuts such as cashews, almonds, and pine nuts; and seeds like pumpkin, sesame, and flaxseeds.
6. Decrease Saturated Fats:
A diet high in saturated fat is detrimental to fertility, as it can contribute to hormonal imbalances and increase inflammation throughout the body. Both of these can hinder the production of healthy cervical mucus and impair fertility.

To promote healthy cervical mucus, it’s essential to reduce saturated fat intake from sources such as fatty meats, processed meats like sausages, hot dogs, bacon, and deli meats, excessive consumption of full-fat dairy products, lard, deep-fried foods, baked goods, and snack foods like potato chips and crackers.
To learn more about the five top fertility-boosting foods, dive in more in previous blog posts here.
7. Decrease Alcohol And Caffeine:
Alcohol and caffeine may negatively impact cervical mucus production due to their dehydrating effects. These substances possess diuretic properties, which cause increased urination and consequently lead to more significant fluid loss in the body.
Heavy alcohol consumption, in particular, can disrupt the menstrual cycle, potentially affecting cervical mucus. To mitigate these effects, it’s essential to limit your intake of alcohol and caffeine while ensuring you drink sufficient water to stay well-hydrated.
Bottom Line:
- Healthy cervical mucus provides an ideal environment for sperm survival and transport to the egg, directly influencing fertility.
- Monitoring changes in cervical mucus can help identify a woman’s fertile window.
- Stay hydrated, consume healthy carbohydrates and fats, and increase your vitamin C, E, and zinc intake to support healthy cervical mucus production.
- Limit alcohol and caffeine consumption to prevent dehydration, which can negatively impact cervical mucus production.
