Understanding Fertility Hormones and Their Role in Conception
Fertility hormones play a pivotal role in a woman’s reproductive system, orchestrating the menstrual cycle and influencing the chances of conception. This delicate hormonal balance determines ovulation, egg health, and reproductive health.
Whether you’re trying to conceive naturally or undergoing fertility treatments, understanding these key fertility hormones—oestrogen, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), and progesterone—can empower women to take control of their fertility journey.
This blog will explore the essential fertility hormones, their functions, and how they impact ovulation, egg health, and overall pregnancy success.
The Four Key Fertility Hormones
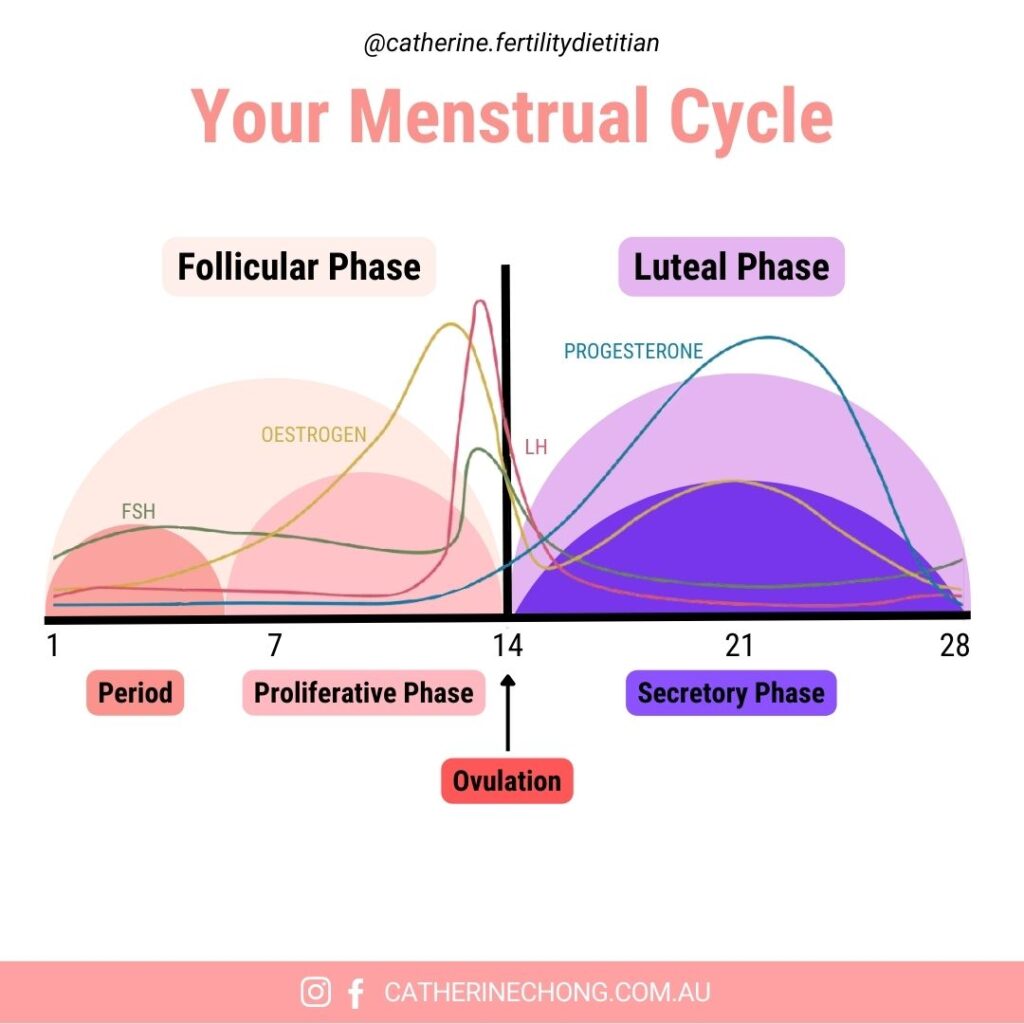
1. Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH): The Egg Development Hormone
The pituitary gland produces follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and plays a crucial role in ovarian follicle development. These follicles house oocytes, which have the potential to become mature eggs ready for fertilisation.
- Function: Stimulates ovarian follicles to grow and mature
- Peak Levels: During the early follicular phase and before ovulation
- Impact on Fertility: Adequate FSH levels are essential for healthy egg development and ovulation
FSH also triggers the production of oestrogen, another key fertility hormone that supports ovulation and uterine lining preparation.
2. Oestrogen: The Hormone for Ovulation and Fertile Cervical Mucus
Oestrogen, predominantly produced by the ovaries, is a vital hormone that regulates various aspects of fertility.
- Function: Supports egg maturation and enhances cervical mucus quality
- Peak Levels: Right before ovulation
- Impact on Fertility: Promotes an optimal environment for sperm survival and egg fertilisation
As follicles mature, oestrogen levels rise, reaching a threshold that triggers the release of luteinizing hormone (LH), a critical step in ovulation.
3. Luteinizing Hormone (LH): The Ovulation Trigger
Luteinizing hormone (LH) surges around the middle of the menstrual cycle, prompting ovulation.
- Function: Triggers the release of a mature egg from the dominant follicle
- Peak Levels: Mid-cycle, typically around day 14 in a 28-day cycle
- Impact on Fertility: Essential for ovulation, allowing sperm to fertilise an egg
Following ovulation, LH transforms the ruptured follicle into the corpus luteum, producing progesterone to support early pregnancy.
4. Progesterone: The Pregnancy-Supporting Hormone
Progesterone is produced by the corpus luteum after ovulation and is essential for preparing the uterus for a potential pregnancy.
- Function: Thickens and maintains the uterine lining for implantation
- Peak Levels: During the luteal phase (after ovulation)
- Impact on Fertility: Supports early pregnancy; if pregnancy does not occur, progesterone levels drop, leading to menstruation
Can You Influence Your Fertility Hormones?
Yes! Hormonal balance is crucial in reproductive health, and lifestyle choices can significantly impact fertility hormones.
How to Support Fertility Hormone Balance Naturally
- Follow a personalised fertility nutrition plan: A nutrient-rich diet with antioxidants, fibre, and lean proteins helps regulate hormone levels and support egg quality. Working with a fertility dietitian through our fertility nutrition assessment and tailored supplement plan ensures that you receive the precise nutrients your body needs, significantly enhancing your chances of conception.

- Exercise in Moderation: Regular physical activity helps manage insulin levels and supports hormonal equilibrium. However, excessive exercise can disrupt menstrual cycles.

- Manage Stress: High-stress levels can lead to hormonal imbalances, affecting ovulation and cycle regularity. Mindfulness, meditation, and gentle movement can support stress reduction.

- Prioritise Quality Sleep: Sleep plays a crucial role in hormone regulation. Aim for 7–9 hours of restorative sleep per night to optimise fertility hormone function.

- Avoid Hormone Disruptors: Smoking, excessive alcohol, and environmental toxins (like BPA and pesticides) can negatively impact fertility hormones. Reducing exposure can help maintain hormonal balance.

The Bottom Line
- Fertility hormones—FSH, oestrogen, LH, and progesterone—work together to regulate the menstrual cycle and support conception.
- Understanding how these hormones function and adopting a fertility-friendly lifestyle can significantly improve your fertility.
